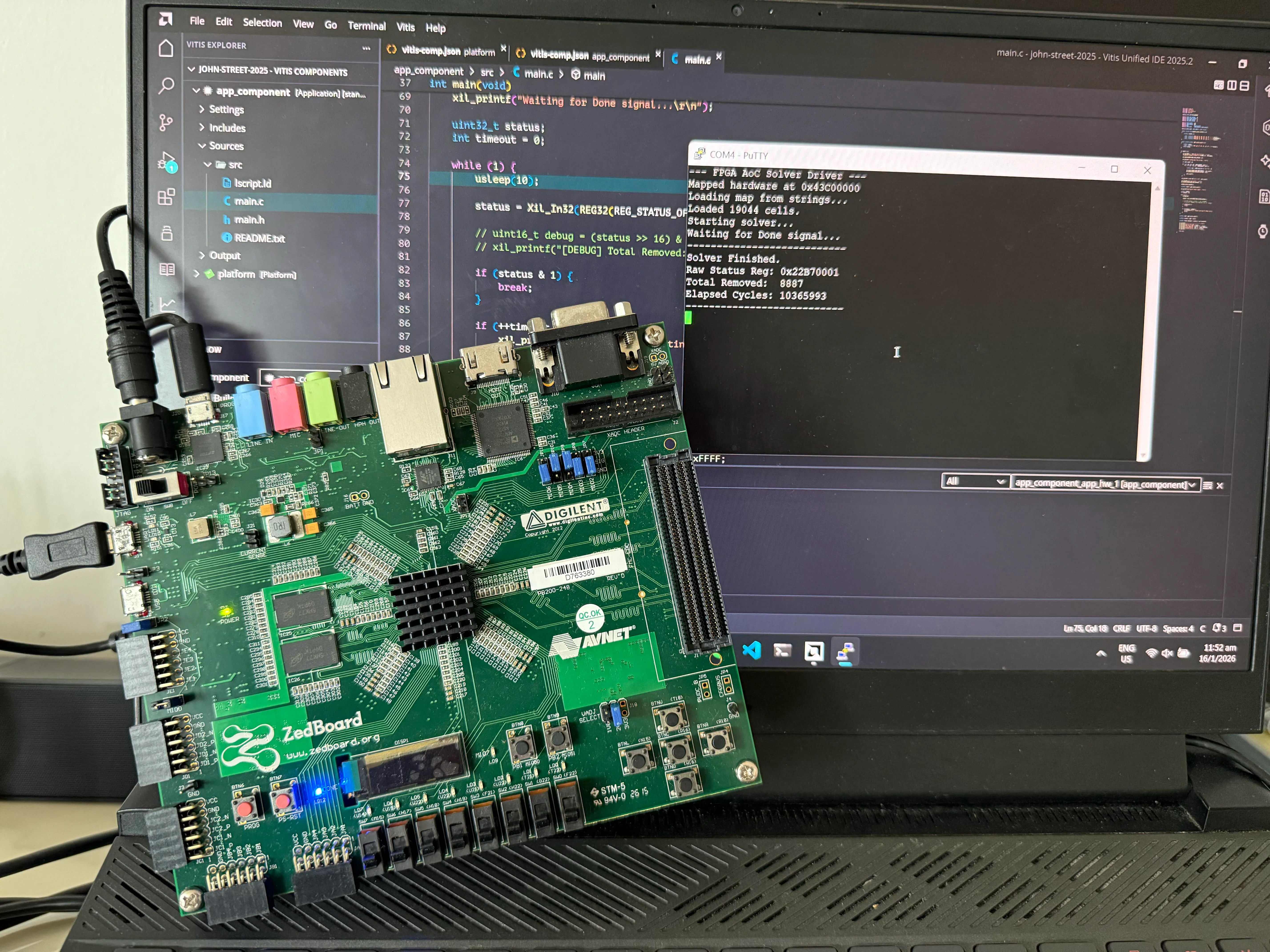
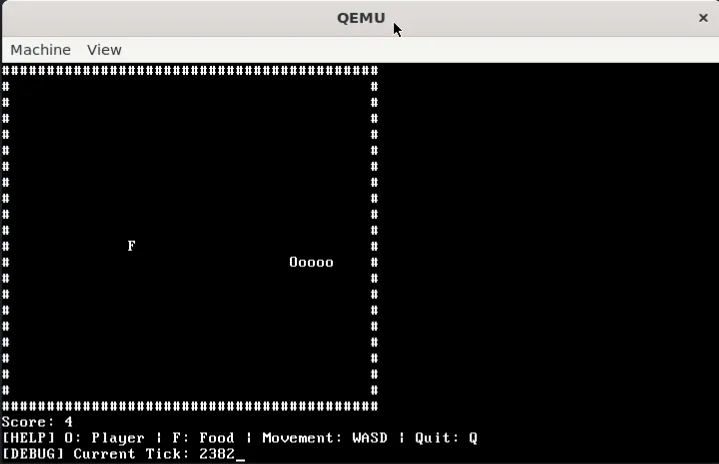
I build things, I break things. Part-time programmer , part-time CTF player . Proficient in Python, decent in Rust and C++. Apart from programming, I attempt web exploitation challenges in CTFs and do a bit of binary exploitation (pwn) on the side.
Currently exploring hardware and programming languages, but my interests often vary. I believe that both breadth and depth are crucial for innovation — depth fosters mastery while breadth opens up new avenues for creativity by combining different concepts.
Most of my previous endeavours can be found in my GitHub , and I've pinned some personal favourites in the projects mentioned in my resume.